7 Powerful Green Energy Initiatives Transforming Our Future Sustainably
“7 Powerful Green Energy Initiatives Transforming Our Future Sustainably”
“Discover 7 powerful green energy initiatives transforming our future sustainably. Explore innovations in solar, wind, hydrogen, geothermal, and more for a cleaner planet.”
Green Energy Initiatives :
7 Powerful Green Energy Initiatives Transforming Our Future Sustainably
As the world faces growing environmental challenges, green energy initiatives are becoming more crucial than ever. Sustainable energy solutions not only reduce carbon footprints but also create a cleaner and healthier planet. Governments, businesses, and individuals are actively investing in renewable energy sources to combat climate change and build a more resilient future.

In this article, we explore seven powerful green energy initiatives that are transforming the way we produce and consume energy.
1. Solar Power Revolution
Solar energy is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy sources. Thanks to breakthroughs in photovoltaic technology, modern solar panels now offer greater efficiency at a more affordable cost. Countries like China, the United States, and India are leading the way in large-scale solar farms.
Key Benefits: Green Energy Initiatives
Zero Carbon Emissions – Solar power reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Cost-Effective – Lower electricity bills and tax incentives.
Scalability – Can be installed on rooftops or used for large solar farms.
Notable Initiative:
The Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex in Morocco is the world’s largest concentrated solar power plant, generating over 580 MW of electricity, enough to power millions of homes.
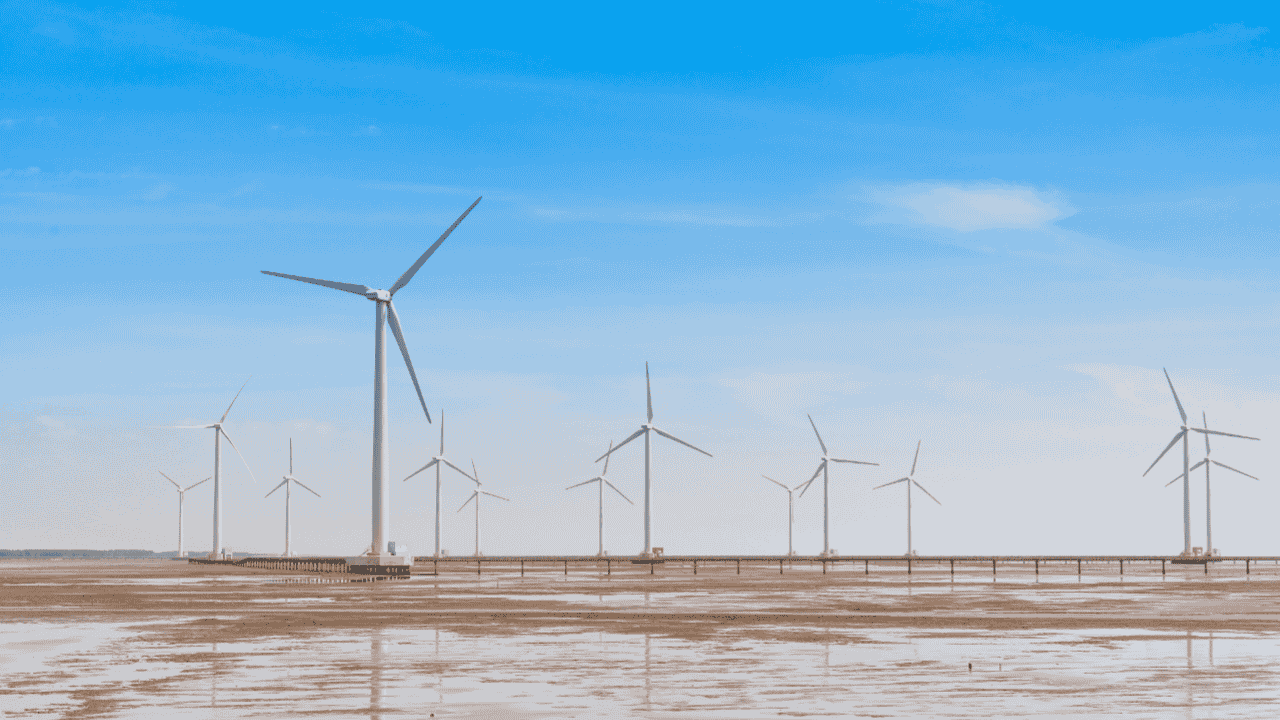
2. Wind Energy Expansion
Wind power is another crucial renewable energy source that is reshaping the global energy landscape. With offshore and onshore wind farms, wind turbines generate massive amounts of electricity with minimal environmental impact.
Key Benefits:
High Efficiency – Modern wind turbines are more efficient than ever.
Land Utilization – Can be installed on farmland without affecting agriculture.
Job Creation – The wind industry creates thousands of new jobs.
Notable Initiative:
The Hornsea Wind Farm in the UK is the world’s largest offshore wind farm, capable of producing over 1.2 GW of electricity, enough to power over one million homes.
3. Hydropower Innovations
Hydropower has been a reliable source of renewable energy for decades. However, modern innovations such as small-scale hydro and run-of-river systems are making it even more sustainable.
Key Benefits:
Reliable & Consistent – Unlike solar and wind, hydropower is available 24/7.
Energy Storage – Hydroelectric dams can store water and release it when needed.
Long Lifespan – Hydropower plants can last for decades with proper maintenance.
Notable Initiative:
The Itaipu Dam between Brazil and Paraguay generates nearly 103 TWh of electricity annually, supplying 90% of Paraguay’s electricity needs.
4. Green Hydrogen Development
Green hydrogen, produced using renewable electricity, is emerging as a game-changer for clean energy storage and industrial applications. Unlike traditional hydrogen production, green hydrogen produces zero emissions.
Key Benefits:
Versatile – Can be used for transportation, industry, and power generation.
Long-Term Storage – Can store excess renewable energy.
Zero Pollution – Only emits water vapor when used.
Notable Initiative:
The Hydrogen Council is a global initiative working toward making hydrogen a mainstream energy source. Nations such as Germany and Japan are making significant investments in hydrogen infrastructure to drive the clean energy transition.
5. Geothermal Energy Expansion
Geothermal power taps into the Earth’s internal heat to generate sustainable electricity. Unlike wind or solar, it provides constant, reliable power without fluctuations.
Key Benefits:
Sustainable & Renewable – Uses Earth’s natural heat.
Minimal Land Footprint – Requires less space than other renewables.
Cost-Effective – Low operating costs over time.
Notable Initiative:
Iceland, known as the global leader in geothermal energy, produces nearly 90% of its electricity from geothermal and hydro sources.
6. Bioenergy and Waste-to-Energy Projects
Bioenergy uses organic materials like crop waste, algae, and municipal waste to generate power. It is an eco-friendly way to manage waste while producing clean energy.
Key Benefits:
Reduces Landfill Waste – Converts trash into useful energy.
Carbon-Neutral – Bioenergy recycles CO₂ that plants absorbed during growth.
Diverse Applications – Used for electricity, heating, and even biofuels.
Notable Initiative:
Sweden’s waste-to-energy program has been so successful that the country imports waste from other nations to generate electricity and heat.
7. Smart Grid and Energy Storage Technologies
A smart grid integrates renewable energy with digital monitoring to optimize electricity distribution. Coupled with advanced battery storage, it ensures a stable and efficient energy supply.
Key Benefits:
Reduces Blackouts – Stores surplus energy for peak demand.
Supports Renewable Energy – Manages fluctuations in solar and wind power.
Lower Costs – Increases grid efficiency and reduces energy waste.
Notable Initiative:
Tesla’s Megapack Battery Storage Systems help stabilize grids by storing renewable energy and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Final Thoughts
The transition to Green Energy Initiatives is no longer a choice—it is a necessity. These seven powerful initiatives are shaping a sustainable future by reducing carbon emissions, creating jobs, and making renewable energy more accessible worldwide.
With continued investments and innovation, the dream of a 100% clean energy future is closer than ever. Are you ready to embrace the green energy revolution?
Green Energy Initiatives : Paving the Way to a Sustainable Future
In an era marked by climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation, the global shift toward green energy initiatives has become more than a trend—it’s a necessity. Governments, corporations, and individuals worldwide are embracing renewable energy solutions to reduce carbon footprints, combat global warming, and secure a cleaner future. This article explores the transformative power of green energy, its benefits, challenges, and the innovations driving this critical movement.
The Rise of Green Energy Initiatives : What’s Fueling the Transition?
Green Energy Initiatives , derived from natural sources like sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat, offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. The urgency to adopt these resources stems from two pressing issues:
Climate Crisis: Fossil fuels account for over 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning to renewables is vital to limit temperature rises to 1.5°C, as outlined in the Paris Agreement.
Energy Security: Renewable resources are inexhaustible, reducing reliance on geopolitically unstable regions for oil and gas.
Countries like Germany, Denmark, and Costa Rica have already made strides, with renewables supplying over 40% of their energy mix. Meanwhile, solar and wind power costs have plummeted by 80% and 60%, respectively, in the last decade, making them economically viable.
Key Green Energy Initiatives Shaping the Future
Solar Power Innovations:
From rooftop panels to massive solar farms, photovoltaic technology is revolutionizing energy access. India’s Bhadla Solar Park and Morocco’s Noor Complex exemplify large-scale projects powering millions of homes. Emerging technologies like perovskite solar cells promise even higher efficiency at lower costs.
Wind Energy Expansion:
Offshore wind farms, such as the UK’s Hornsea Project, harness stronger, steadier winds at sea. Advances in turbine design and floating platforms are unlocking potential in deeper waters.
Hydropower and Geothermal Solutions:
While hydropower remains the largest renewable source, geothermal energy is gaining traction in volcanic regions like Iceland and Kenya, providing reliable baseload power.
Green Hydrogen:
Produced via electrolysis using renewable electricity, green hydrogen is emerging as a clean fuel for industries and transportation, with the EU and Japan leading investments.
Bioenergy and Waste-to-Energy Projects:
Converting agricultural waste, algae, and municipal trash into energy reduces landfill use and emissions. Sweden recycles 99% of its waste, with half being converted to energy.
Benefits Beyond the Environment
Green energy initiatives deliver multifaceted advantages:
Economic Growth: The renewable sector employs over 12 million people globally, fostering job creation in manufacturing, installation, and R&D.
Health Improvements: Reducing air pollution from coal plants could prevent 4.5 million premature deaths annually.
Energy Equity: Decentralized solar systems empower remote communities, bridging the energy access gap for 760 million people lacking electricity.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite progress, obstacles persist:
Intermittency: Solar and wind depend on weather. Solutions include battery storage (e.g., Tesla’s Powerwall), grid modernization, and hybrid systems combining multiple renewables.
High Initial Costs: Governments are offsetting this through subsidies, tax credits, and green bonds. The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act allocates $369 billion for clean energy incentives.
Infrastructure Gaps: Developing nations need funding and technology transfers. Initiatives like the UN’s Sustainable Energy for All aim to address these disparities.

The Role of Policy and Global Collaboration
Effective policies accelerate adoption. Examples include:
Carbon Pricing: Putting a price on emissions encourages businesses to switch to renewables.
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): Mandating utilities to source a percentage of energy from renewables.
International Agreements: The Paris Agreement and COP summits foster accountability and knowledge-sharing.
How Individuals Can Contribute
Collective action drives change. Everyday steps include:
Installing solar panels or opting for green energy tariffs.
Reducing energy consumption via LED lighting, smart thermostats, and energy-efficient appliances.
Advocating for local renewable projects and supporting eco-conscious businesses.
The Road Ahead: A Clean Energy Revolution
The transition to green energy is no longer optional—it’s imperative. With advancements in AI-driven grid management, next-gen nuclear fusion, and circular economy practices, the goal of a net-zero future is within reach. By prioritizing innovation, equity, and collaboration, humanity can ensure a livable planet for generations to come.
Green energy initiatives are reshaping economies, ecosystems, and lives. While challenges remain, the combined efforts of governments, industries, and citizens are creating a blueprint for sustainability.
Embracing renewables isn’t just about saving the planet; it’s about building a resilient, equitable, and prosperous world. The time to act is now—every watt of clean energy brings us closer to a brighter tomorrow.
why have so many governments chosen to subsidize green energy initiatives
Governments around the world have chosen to subsidize green energy initiatives for several key reasons:
1. Combat Climate Change
Fossil fuels are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global warming. By subsidizing renewable energy, governments aim to reduce carbon footprints and meet climate goals such as the Paris Agreement.
2. Energy Security & Independence
Renewable energy reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels, making countries less vulnerable to global oil price fluctuations and geopolitical tensions.
3. Job Creation & Economic Growth
The green energy sector generates millions of jobs in solar, wind, and other renewable industries. Investing in renewables boosts local economies and creates long-term employment opportunities.
4. Cost Reduction & Market Growth
Subsidies help bring down the initial costs of renewable technologies, making them more accessible to businesses and households. As demand grows, production scales up, further lowering costs.
5. Public Health Benefits
Burning fossil fuels releases harmful pollutants that cause respiratory diseases and other health issues. Green energy reduces air pollution, leading to healthier populations and lower healthcare costs.
6. Encouraging Innovation
Funding and incentives drive research and development in clean energy, leading to breakthrough technologies like advanced battery storage, green hydrogen, and smart grids.
7. Meeting Renewable Energy Targets
Many countries have committed to reaching net-zero emissions or increasing their renewable energy share. Subsidies help accelerate the transition and ensure policy goals are met.
By investing in green energy, governments are paving the way for a more sustainable, resilient, and economically viable future.
green energy initiatives meaning
Green Energy Initiatives: Meaning and Purpose
Green energy initiatives refer to policies, projects, and actions aimed at transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable, sustainable energy sources. These initiatives prioritize reducing greenhouse gas emissions, minimizing environmental harm, and promoting energy systems that rely on natural, replenishable resources like sunlight, wind, water, geothermal heat, and bioenergy.
Core Objectives of Green Energy Initiatives
Combat Climate Change: Replace carbon-intensive energy sources (coal, oil, gas) with clean alternatives to cut CO2 emissions.
Promote Sustainability: Ensure energy production meets current needs without compromising future generations’ resources.
Enhance Energy Security: Reduce dependence on finite, imported fossil fuels by leveraging locally available renewables.
Drive Economic Growth: Create jobs in renewable energy sectors like solar panel manufacturing, wind farm installation, and green tech innovation.
Improve Public Health: Lower air and water pollution linked to fossil fuel extraction and combustion.
Key Components of Green Energy Initiatives
Renewable Energy Adoption: Scaling solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal, and biomass energy infrastructure.
Energy Efficiency Measures: Upgrading buildings, transportation, and industries to use less energy.
Policy and Funding: Governments implement laws (e.g., carbon taxes, renewable energy mandates) and allocate subsidies to accelerate clean energy adoption.
Technological Innovation: Research into advanced batteries, green hydrogen, smart grids, and carbon capture.
Community Engagement: Educating and empowering individuals to adopt renewables (e.g., rooftop solar, electric vehicles).
Examples of Green Energy Initiatives
National Level: The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (2022), which invests $369 billion in renewable energy tax credits and climate projects.
Corporate Level: Google’s commitment to run entirely on carbon-free energy by 2030.
Local Level: Community solar programs that allow households to share renewable energy benefits.
Why Are They Important?
Fossil fuels still supply about 80% of global energy, contributing to rising temperatures, extreme weather, and biodiversity loss. Green energy initiatives address these crises by:
Decarbonizing Energy Systems: Renewables produce little to no emissions during operation.
Empowering Underserved Regions: Solar microgrids provide electricity to remote areas without traditional grid access.
Future-Proofing Economies: Investing in renewables avoids stranded assets as fossil fuels phase out.
In essence, green energy initiatives are a global response to the urgent need for cleaner, equitable, and resilient energy systems. They represent a shift from exploiting finite resources to harnessing Earth’s natural energy flows, ensuring a healthier planet and sustainable development.
Green Energy Initiatives 2025
Green Energy Initiatives in 2025: A Global Roadmap for Sustainability
As the world races to meet climate goals and transition to cleaner energy systems, 2025 is poised to be a pivotal year for green energy initiatives. Governments, corporations, and innovators are doubling down on strategies to accelerate decarbonization, scale renewables, and address lingering challenges. Here’s an in-depth look at what to expect in 2025 and how these initiatives will shape the future of energy.
1. Accelerated Renewable Energy Deployment
By 2025, renewable energy capacity is projected to grow by 50% compared to 2020 levels, driven by solar, wind, and hydropower. Key developments include:
Solar Power Dominance: Solar installations will surge, with countries like China, India, and the U.S. leading the charge. Innovations like bifacial solar panels and agrivoltaics (combining agriculture with solar farms) will maximize land efficiency.
Offshore Wind Expansion: Europe’s North Sea and the U.S. East Coast will host massive offshore wind projects. The UK’s Dogger Bank Wind Farm, set to power 6 million homes by 2025, exemplifies this trend.
Hydropower Modernization: Aging dams will be retrofitted with eco-friendly turbines, while small-scale hydro projects will electrify remote regions in Africa and Southeast Asia.
2. Green Hydrogen Goes Mainstream
2025 is expected to mark the tipping point for green hydrogen (produced using renewable energy). Initiatives include:
EU’s Hydrogen Backbone: Europe plans to build a 6,800 km hydrogen pipeline network by 2025, linking renewable hubs to industrial zones.
Australia’s Export Ambitions: Projects like the Asian Renewable Energy Hub aim to produce 1.75 million tons of green hydrogen annually for export to Japan and South Korea.
Industrial Decarbonization: Steel, shipping, and aviation giants like Maersk and Airbus will pilot hydrogen-powered vessels and aircraft.
3. Energy Storage Breakthroughs
Battery storage capacity is projected to quadruple by 2025, addressing renewable intermittency:
Solid-State Batteries: Companies like Toyota and QuantumScape plan to commercialize solid-state batteries, offering faster charging and longer lifespans for EVs and grids.
Grid-Scale Storage: The U.S. and China will deploy massive lithium-ion and flow battery systems to stabilize grids. California’s Moss Landing Expansion, a 3 GWh facility, will power 225,000 homes during peak demand.

Second-Life Batteries: Recycled EV batteries will be repurposed for residential and industrial storage, reducing waste.
4. Policy Levers Driving Change
Governments are rolling out aggressive policies to meet 2025 milestones:
Carbon Pricing: Over 25 countries will implement carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, making fossil fuels costlier. Canada’s carbon tax, for instance, will rise to CAD 170/ton by 2025.
Phase-Out Deadlines: Nations like Germany and the UK will shutter coal plants by 2025, replacing them with renewables and gas-to-hydrogen transitions.
Subsidies and Tax Credits: The U.S. Inflation Reduction Act’s incentives for solar, wind, and EVs will catalyze $1.2 trillion in private investments by 2025.
5. Corporate Net-Zero Commitments
By 2025, over 70% of Fortune 500 companies will have net-zero targets, backed by concrete actions:
RE100 Expansion: Tech giants like Apple and Microsoft will achieve 100% renewable energy use for operations, pushing suppliers to follow suit.
Circular Economy Models: Automakers like Tesla and Volvo will ramp up EV battery recycling, aiming for 95% material recovery rates.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF): Airlines like Delta and United will blend 10% SAF into flights, cutting aviation emissions by 15%.
6. Emerging Markets Take the Lead
Developing nations are leapfrogging fossil fuels through decentralized solutions:
Africa’s Solar Revolution: Initiatives like Kenya’s Last Mile Connectivity Project will deploy solar mini-grids to electrify 25 million people by 2025.
India’s Green Corridors: Dedicated transmission lines will integrate 500 GW of renewables into the grid, reducing reliance on coal.
Latin American Innovations: Brazil and Chile will leverage wind-solar hybrids and green hydrogen to power mining and agriculture sectors.
7. Challenges to Overcome
While progress is promising, hurdles remain:
Supply Chain Bottlenecks: Critical mineral shortages (e.g., lithium, cobalt) may delay battery and solar panel production.
Grid Infrastructure Gaps: Aging grids in the U.S. and Europe need $2 trillion in upgrades to handle renewable influx.
Policy Fragmentation: Inconsistent regulations across regions could slow global collaboration.
The Bottom Line: A Year of Action
2025 will be a defining year for green energy, blending ambition with execution. Success hinges on:
Public-Private Partnerships: Governments and firms must co-fund R&D and infrastructure.
Equitable Transitions: Ensuring developing nations access funding and technology.
Consumer Engagement: Encouraging households to adopt rooftop solar, EVs, and energy-efficient practices.
From hydrogen highways to AI-optimized grids, the green energy landscape in 2025 will reflect humanity’s collective resolve to combat climate change. While challenges persist, the momentum is undeniable—the race to a sustainable future is accelerating, and 2025 will be a milestone worth watching.
green energy initiatives and carbon footprint reduction
Green Energy Initiatives and Carbon Footprint Reduction
Introduction
In recent years, the global push towards sustainability has gained significant momentum. Climate change, largely driven by carbon emissions from human activities, has led to rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and environmental degradation.
To combat these issues, green energy initiatives have emerged as a crucial solution. These initiatives focus on utilizing renewable energy sources while simultaneously reducing the carbon footprint of industries, households, and transportation systems. Transitioning to sustainable energy not only benefits the environment but also promotes economic growth, energy security, and public health.
Understanding Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint refers to the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs), particularly carbon dioxide (CO₂), released into the atmosphere as a result of human activities. It includes emissions from burning fossil fuels, industrial processes, agriculture, and deforestation. The carbon footprint of an individual, company, or country is measured in terms of CO₂ equivalent (CO₂e), representing the combined impact of all GHGs. Reducing this footprint is essential to mitigating climate change and ensuring a sustainable future.
Green Energy Initiatives
Green energy refers to energy derived from renewable and non-polluting sources such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. Governments, businesses, and individuals are implementing green energy initiatives to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions. Some key initiatives include:
1. Solar Power Expansion
Solar energy is one of the most accessible and abundant renewable energy sources. Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight into electricity, reducing dependence on coal and gas-fired power plants. Countries like China, the United States, and India are investing heavily in solar farms, while residential solar panels are becoming more affordable due to advancements in technology and government incentives.
2. Wind Energy Development
Wind power harnesses the kinetic energy of wind through turbines to generate electricity. Offshore and onshore wind farms are expanding globally, providing a clean alternative to fossil fuel-based power generation. Countries such as Denmark and Germany are leading the way in wind energy adoption, with wind contributing a significant share of their electricity production.
3. Hydropower and Tidal Energy
Hydropower, generated from the movement of water through dams, has long been a reliable source of renewable energy. However, modern developments in tidal and wave energy are opening new possibilities for sustainable electricity generation. Unlike solar and wind, tidal energy is predictable, making it a stable energy source.
4. Geothermal Energy Utilization
Geothermal energy harnesses the Earth’s natural heat from beneath the surface to produce electricity and supply direct heating. Countries with significant geothermal resources, such as Iceland and the Philippines, have successfully integrated this energy source into their power grids, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels.
5. Bioenergy and Sustainable Biomass
Biomass energy involves using organic materials like agricultural waste, wood pellets, and algae to produce biofuels and biogas. This form of energy is renewable and can help in waste management while reducing carbon emissions from conventional fuels. Sustainable biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, are also being used in transportation as an alternative to gasoline and diesel.
Strategies for Reducing Carbon Footprint
While transitioning to green energy is a significant step, individuals and businesses must also adopt strategies to minimize their carbon footprint in daily activities. Some key measures include:
1. Energy Efficiency Improvements
Upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, LED lighting, and smart thermostats can reduce energy consumption in homes and offices. Industries can optimize production processes to cut down on energy waste and emissions.
2. Sustainable Transportation
Electric vehicles (EVs), public transit systems, cycling, and carpooling are effective ways to reduce transportation-related emissions. Governments are also investing in EV charging infrastructure and promoting the use of hydrogen fuel cells for cleaner mobility.
3. Afforestation and Reforestation
Trees absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere, making afforestation (planting new trees) and reforestation (restoring forests) vital for carbon sequestration. Urban green spaces, vertical gardens, and tree-planting campaigns can enhance sustainability efforts.
4. Reducing Waste and Promoting Recycling
Waste management plays a crucial role in carbon footprint reduction. Landfills release methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Recycling, composting, and reducing single-use plastics help mitigate waste-related emissions. Businesses adopting a circular economy approach, where products are reused and repurposed, contribute to sustainability.
5. Sustainable Agriculture and Diet Choices
Agriculture contributes to carbon emissions through deforestation, fertilizer use, and methane from livestock. Sustainable farming practices, such as organic farming, crop rotation, and agroforestry, help reduce emissions. Additionally, plant-based diets and locally sourced foods lower the environmental impact of food production.
6. Corporate Responsibility and Green Policies
Businesses are integrating corporate sustainability strategies to lower their carbon footprint. Many companies are committing to carbon neutrality by adopting renewable energy, carbon offset programs, and green supply chain practices. Governments are also implementing carbon pricing, emission reduction targets, and incentives for green innovation.
Benefits of Green Energy and Carbon Footprint Reduction
1. Environmental Protection – Reducing reliance on fossil fuels decreases air and water pollution, preserving ecosystems and biodiversity.
2. Climate Change Mitigation – Lower carbon emissions slow global warming, reducing the frequency of extreme weather events.
3. Energy Security – Renewable energy diversifies the energy mix, reducing dependence on imported fuels and stabilizing energy prices.
4. Economic Growth and Job Creation – The green energy sector creates employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
5. Public Health Improvement – Reduced air pollution leads to lower rates of respiratory diseases, improving overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
Green energy initiatives and carbon footprint reduction efforts are essential for a sustainable and livable future. Governments, businesses, and individuals all have a role to play in transitioning to renewable energy sources and adopting eco-friendly practices.
By investing in clean energy, improving energy efficiency, and making sustainable choices in transportation, waste management, and agriculture, we can significantly cut carbon emissions. As the world moves toward a greener economy, embracing these changes will not only protect the environment but also ensure economic resilience and a healthier society for future generations